1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62 |
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">/* TextFile Sender: Written by Scott C on 5th April 2013
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);"> using Processing Version 2.0b8 */
import processing.serial.*;
Serial comPort;
style="color: rgb(43, 145, 175);">int counter=0;
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">// Helps to keep track of values sent.
style="color: rgb(43, 145, 175);">int numItems=0;
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//Keep track of the number of values in text file
boolean sendStrings=
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">false;
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//Turns sending on and off
StringLoader sLoader;
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//Used to send values to Arduino
style="color: rgb(43, 145, 175);">void setup(){
comPort =
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">new Serial(
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">this, Serial.list()[0], 9600);
background(255,0,0);
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//Start with a Red background
}
style="color: rgb(43, 145, 175);">void draw(){
}
style="color: rgb(43, 145, 175);">void mousePressed() {
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//Toggle between sending values and not sending values
sendStrings=!sendStrings;
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//If sendStrings is True - then send values to Arduino
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">if(sendStrings){
background(0,255,0);
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//Change the background to green
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">/*When the background is green, transmit
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);"> text file values to the Arduino */
sLoader=
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">new StringLoader();
sLoader.start();
}
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">else{
background(255,0,0);
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//Change background to red
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//Reset the counter
counter=0;
}
}
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">/*============================================================*/
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">/* The StringLoader class imports data from a text file
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);"> on a new Thread and sends each value once every half second */
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">public
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">class
style="color: rgb(43, 145, 175);">StringLoader extends Thread{
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">public StringLoader(){
style="color: rgb(0, 128, 0);">//default constructor
}
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">public
style="color: rgb(43, 145, 175);">void run() {
String textFileLines[]=loadStrings(
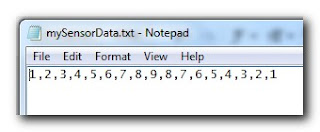
style="color: rgb(163, 21, 21);">"d:/mySensorData.txt");
String lineItems[]=splitTokens(textFileLines[0],
style="color: rgb(163, 21, 21);">",");
numItems=lineItems.length;
style="color: rgb(0, 0, 255);">for(
style="color: rgb(43, 145, 175);">int i = counter; i<numItems; i++){
comPort.write(lineItems[i]);
delay(500);
comPort.write(
style="color: rgb(163, 21, 21);">"0");
}
counter=numItems;
}
}
|