Dumb STB gets smart
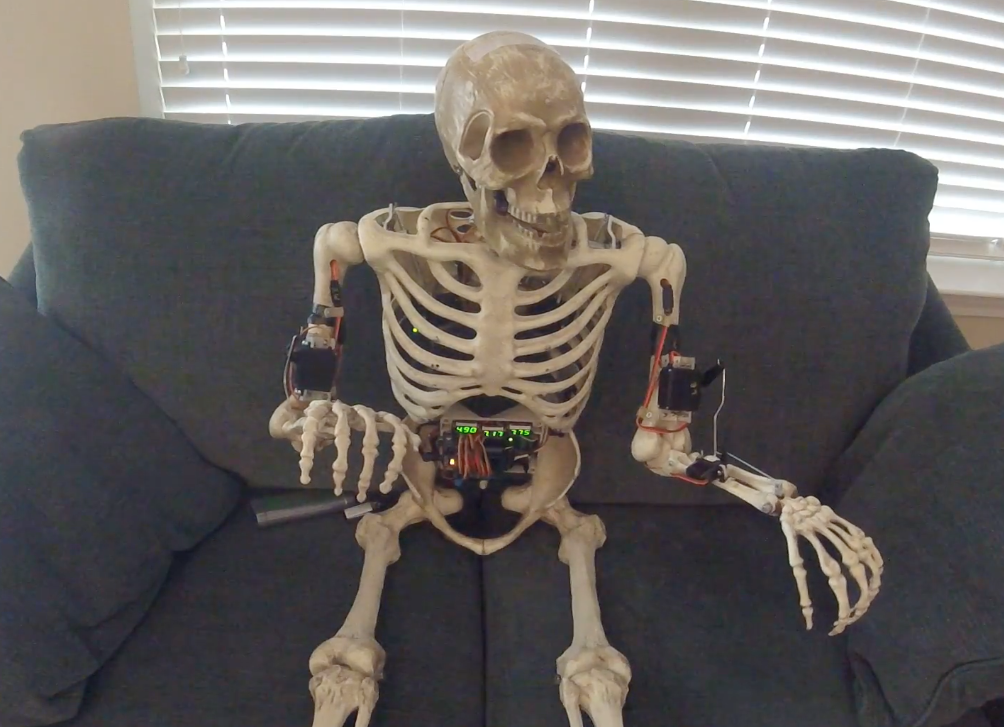
[Vincent Deconinck] gave a fresh lease of life to an old set top box by adding a few Euro’s worth of hardware and some software smarts. The device in question is an old VOOcorder – a Cisco set-top box provided by VOO, his cable service provider in Belgium.
The VOOcorder doesn’t have any WiFi hardware or browser / app based interfaces. It’s a simple device controlled either via an IR remote or front panel buttons. [Vincent] added an ESP8266 and hooked it up to the IR receiver on the set-top box. He also set it up as an SPI slave to the front panel VFD display controller and connected it to the debug serial interface of the VOOcorder as well. The software, on the other hand, required a lot more work consisting of code running on the ESP itself, several HTML pages and JavaScript code for the browser front end, and a few scripts running in the background.
The result was bidirectional interactivity from within a browser, allowing him to send commands and receive status information as well as providing a user-friendly search interface. Further, his browser interface was integrated with information from the service providers website letting him do scheduling and recording of programs. The stuff that interested us is how he sniffed out the IR signals, figured out the SPI protocol used by the front panel controller, and implemented SPI-slave mode for the ESP8266. [Vincent] was surprised that such a cheap device could handle three distinct web servers while parsing two message streams without a hitch.
It’s a great hack showing us how to use super cheap electronics to upgrade and modernize old hardware. Check out the two videos after the break – showing a demo of the hack in action, and a walk through of the hardware modifications.
Filed under: hardware, home entertainment hacks




 Fail of the Week is a Hackaday column which celebrates failure as a learning tool. Help keep the fun rolling by writing about your own failures and
Fail of the Week is a Hackaday column which celebrates failure as a learning tool. Help keep the fun rolling by writing about your own failures and