There’s a mineral called pyrite with a interesting nickname, fool’s gold, because it has a superficial resemblance to gold and it’s by far the most frequently mineral mistaken for gold. Even if it’s pretty abundant, there’s a rare form of pyrite which is crystallised in radial shape (as unusual disc spherulites), taking the shape of a disc. The amazing fact is that the only deposit where pyrites of such morphology are found is in Illinois (USA) and the discs are dated around 300 million years ago!
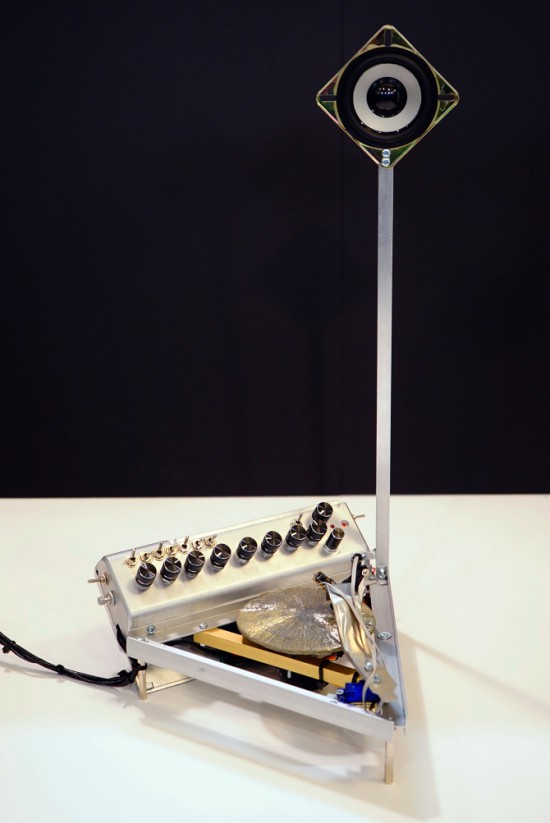
Dmitry Morozov (aka ::vtol::), a media artist living in Moscow, had the chance to use a pyrite disc and created Ra, a sound object / synthesizer running on Arduino Nano. Ra uses laser for scanning the irregularities of the surface of the disc and further transforms this data to produce sound:
This project originated as a result of an interesting set of circumstances – a pyrite disc was given to me as a gift by a mineral seller in Boulder city (USA). Upon hearing about my works, she asked to do something with such crystal, and refused to take payment for getting it. In the same period, I was reading articles on various ways of archiving and preservation of sounds from the first, historical sources of the recorded sound – wax discs and other fragile carriers. All technologies were based on the usage of lasers. Inspired by these projects, I set out to create a self-made laser sound reader which would be able to produce sound from various uneven surfaces, using minimal resources to achive it. Thus emerged the idea to construct an instrument using the pyrite disc and a self-made laser sound reader.
The production of the object was possible thanks to the commission of the Sound Museum in St.-Petersburg which now has Ra in its collection.
Check the bill of materials and other details on Dmitry’s website. Explore other projects by Dmitry featured on Arduino Blog.