A Remote for CHDK Cameras Made Possible with Arduino
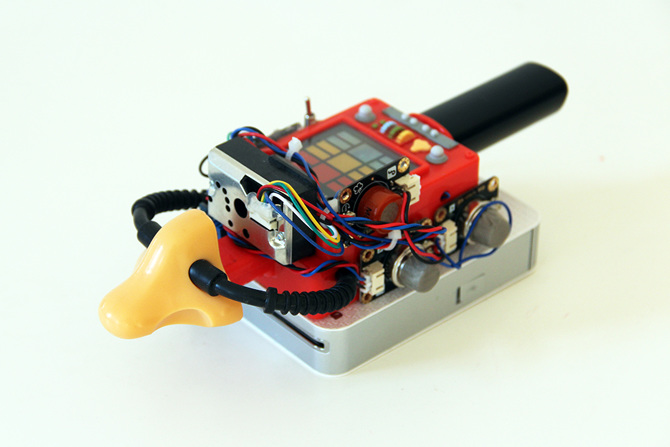
[AlxDroidDev] built himself a nice remote control box for CHDK-enabled cameras. If you haven’t heard of CHDK, it’s a pretty cool software modification for some Canon cameras. CHDK adds many new features to inexpensive cameras. In this case, [AlxDroidDev] is using a feature that allows the camera shutter to be activated via USB. CHDK can be run from the SD card, so no permanent modifications need to be made to the camera.
[AlxDroidDev’s] device runs off of an ATMega328p with Arduino. It operates from a 9V battery. The circuit contains an infrared receiver and also a Bluetooth module. This allows [AlxDroidDev] to control his camera using either method. The device interfaces to the camera using a standard USB connector and cable. It contains three LEDs, red, green, and blue. Each one indicates the status of a different function.
The Arduino uses Ken Shirrif’s IR Remote library to handle the infrared remote control functions. SoftwareSerial is used to connect to the Bluetooth module. The Arduino code has built-in functionality for both Canon and Nikon infrared remote controls. To control the camera via Bluetooth, [AlxDroidDev] built a custom Android application. The app can not only control the camera’s shutter, but it can also control the level of zoom.
Filed under: Arduino Hacks