Bring Precision to the Woodshop with an Electronic Router Lift

One of the knocks that woodworkers get from the metalworking crowd is that their chosen material is a bit… compliant. Measurements only need to be within a 1/16th of an inch or so, or about a millimeter, depending on which side of the Atlantic you’re on. And if you’re off a bit? No worries, that’s what sandpaper is for.
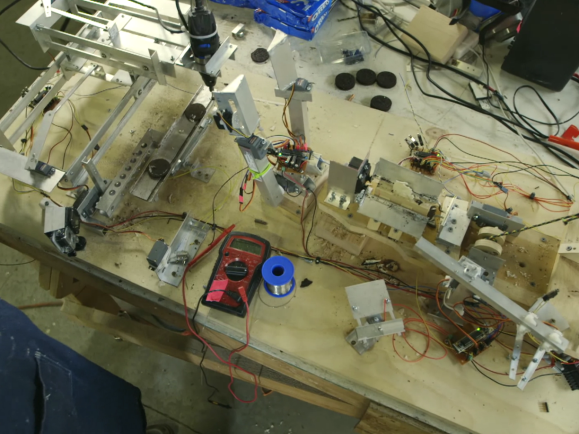
This electronic router lift is intended to close the precision gap and make woodworking a bit less subjective. [GavinL]’s build instructions are clearly aimed at woodworkers who haven’t dabbled in the world of Arduinos and stepper motors, and he does an admirable job of addressing the hesitancy this group might feel when tackling such a build. Luckily, a lot of the mechanical side of this project can be addressed with a commercially available router lift, which attaches to a table-mounted plunge router and allows fine adjustment of the cutting tool’s height from above the table.
What’s left is to add a NEMA 23 stepper to drive the router lift, plus an Arduino to control it. [GavinL] came up with some nice features, like a rapid jog control, a fine adjustment encoder, and the ability to send the tool all the way up or all the way down quickly. Another really nice touch is the contact sensor, which is a pair of magnetic probes that attach temporarily to the tool and a height gauge to indicate touch-off. Check the video below to see it all in action.
One quibble we have with [GavinL]’s setup is the amount of dust that the stepper will be subjected to. He might need to switch out to a dustproof stepper sooner rather than later. Even so, we think he did a great job bridging the gap between mechatronics and woodworking — something that [Matthias Wandel] has been doing great work on, too.
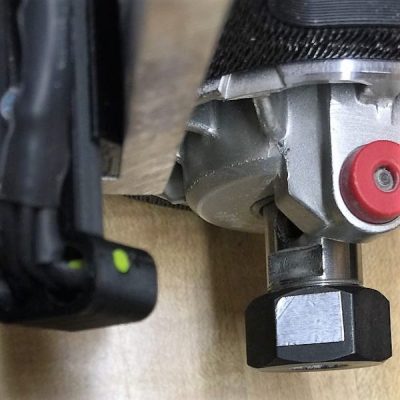

 The CNC router in question is the popular Sienci, and the 3D-printed brackets for the photodiode and LED are somewhat specific for that machine. But [tmbarbour] has included STL files in his exhaustively detailed write-up, so modifying them to fit another machine should be easy. The sensor hangs down just far enough to watch a reflector on one of the flats of the collet nut; we’d worry about the reflector surviving tool changes, but it’s just a piece of shiny tape that’s easily replaced. The sensor feeds into a DIO pin on a Nano, and a small OLED display shows a digital readout along with an analog gauge. The display update speed is decent — not too laggy. Impressive build overall, and we like the idea of using a piece of PLA filament as a rivet to hold the diodes into the sensor arm.
The CNC router in question is the popular Sienci, and the 3D-printed brackets for the photodiode and LED are somewhat specific for that machine. But [tmbarbour] has included STL files in his exhaustively detailed write-up, so modifying them to fit another machine should be easy. The sensor hangs down just far enough to watch a reflector on one of the flats of the collet nut; we’d worry about the reflector surviving tool changes, but it’s just a piece of shiny tape that’s easily replaced. The sensor feeds into a DIO pin on a Nano, and a small OLED display shows a digital readout along with an analog gauge. The display update speed is decent — not too laggy. Impressive build overall, and we like the idea of using a piece of PLA filament as a rivet to hold the diodes into the sensor arm.