Open source microfluidics platform uses Arduino CNC control
Microfluidics deals with the manipulation of tiny amounts of liquid, and as such, specialized equipment must be used for any sort of measurable experimentation. While you could purchase an expensive commercial solution, the Poseidon system—developed by students at the California Institute of Technology—presents an excellent open source option which can be built for a fraction of the cost.
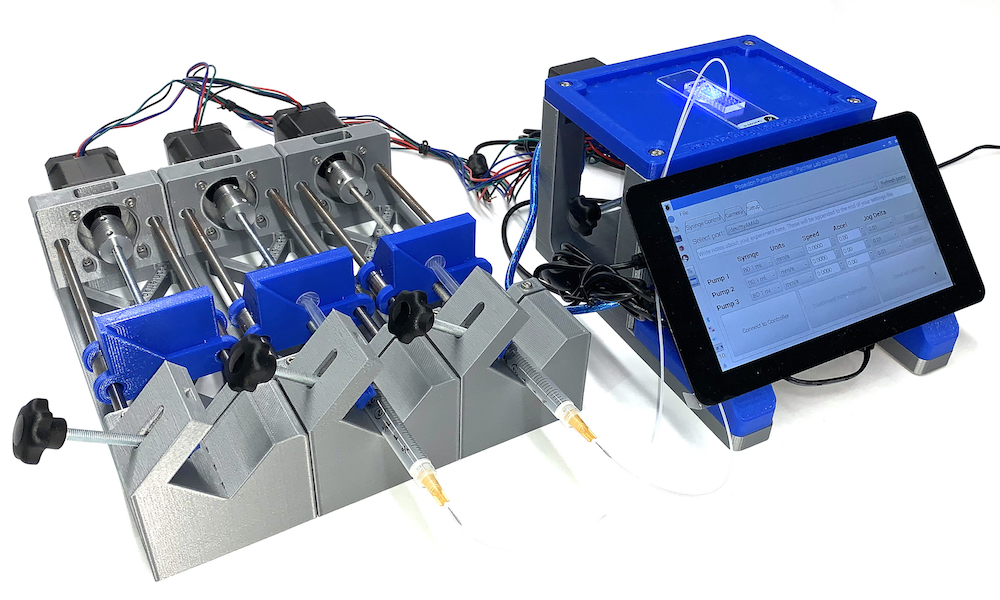
Fluid distribution is managed by a computer GUI or via a terminal window. Steppers handle each of the system’s three “axes,” and push fluid out of syringes under control of an Arduino Uno and CNC shield. A microscope is also available for a full experimental setup.
Specific information on the project can be found on GitHub, and a number of videos on Poseidon team member Sina Booeshaghi’s YouTube page explain things further.
The Poseidon syringe pump and microscope system is an open source alternative to commercial systems. It costs less than $400 and can be assembled in an hour. It uses 3D-printed parts and common components that can be easily purchased either from Amazon or other retailers. The microscope and pumps can be used together in microfluidics experiments, or independently for other applications. The pumps and microscope can be run from a Windows, Mac, Linux, or Raspberry Pi computer with an easy to use GUI.
The Poseidon system was designed to be customizable. It uses the Raspberry Pi and Arduino electronics boards, which are supported by a strong ecosystem of open source hardware and software, facilitating the implementation of new functionalities.
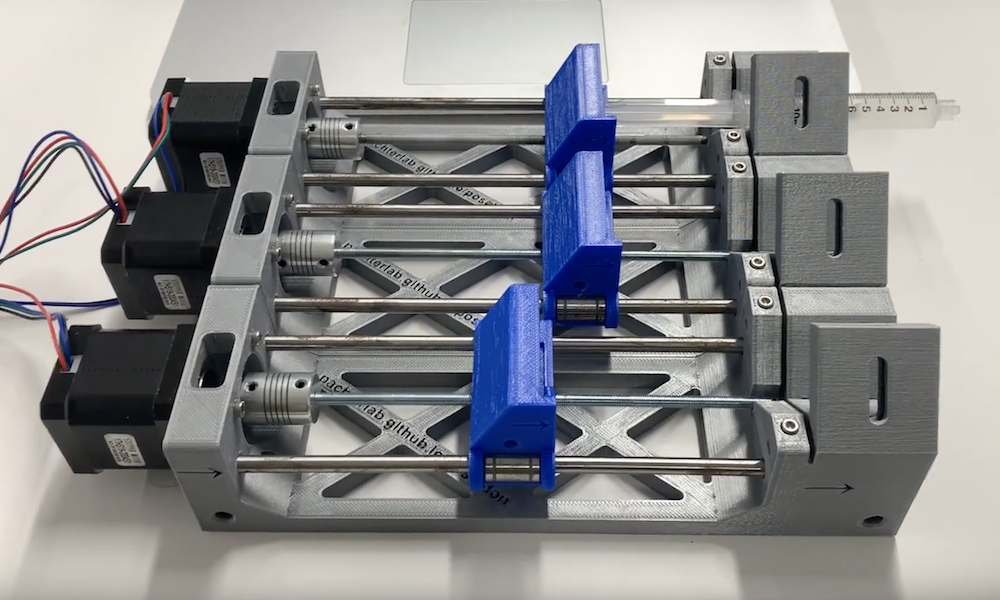
The pump driver uses an Arduino with a CNC shield to run up to three pumps. Each pump has a stepper motor that drives lead screw which in turn moves a sled that is mounted on linear bearings. The displacement of the sled moves the syringe forward or backward allowing the user to dispel or intake liquid.
The controller station uses a Raspberry Pi with a touchscreen to connect to the Arduino and microscope via USB. Because the microscope and Arduino use USB connections, they can alternatively be connected to a computer instead of a Raspberry Pi.

