This cat feeder project by [Ben Millam] is fascinating. It all started when he read about a possible explanation for why house cats seem to needlessly explore the same areas around the home. One possibility is that the cat is practicing its mobile hunting skills. The cat is sniffing around, hoping to startle its prey and catch something for dinner. Unfortunately, house cats don’t often get to fulfill this primal desire. [Ben] thought about this problem and came up with a very interesting solution. One that involves hacking an electronic cat feeder, and also hacking his cat’s brain.
First thing’s first. Click past the break to take a look at the demo video and watch [Ben’s] cat hunt for prey. Then watch in amazement as the cat carries its bounty back to the cat feeder to exchange it for some real food.
[Ben] first thought about hiding bowls of food around the house for his cat to find, but he quickly dismissed this idea after imagining the future trails of ants he would have to deal with. He instead thought it would be better to hide some other object. An object that wouldn’t attract pests and also wouldn’t turn rancid over time. The problem is his cat would have to know to first retrieve the object, then return it to a specific place in order to receive food as a reward. That’s where the cat hacking comes in.
[Ben] started out by training his cat using the clicker method. After all, if the cat couldn’t be trained there was no use in building an elaborate feeding mechanism. He trained the cat to perform two separate behaviors, one tiny bit at a time. The first behavior was to teach the cat to pick up the ball. This behavior was broken down into six micro behaviors that would slowly be chained together.
- Look at the ball
- Approach the ball
- Sniff the ball
- Bite the ball
- Pick up the ball
- Pick up the ball and hold it for a few seconds
[Ben] would press on the clicker and reward his cat immediately upon seeing the desired step of each behavior. Once the cat would perform that step regularly, the reward was removed and only given to the cat if the next step in the chain was performed. Eventually, the cat learned the entire chain of steps, leading to the desired behavior.
Next, [Ben] had to teach his cat about the target area. This was a separately trained behavior that was broken down into the following three steps.
- Look at the target area
- Approach the target area
- Sniff the target area
Once the cat learned both of these behaviors, [Ben] had to somehow link them together. This part took a little bit of luck and a lot of persistence. [Ben] would place the ball near the target area, but not too close. Then, he would reward his cat only when the cat picked up the ball and started moving closer to the target area. There is some risk here that if the cat doesn’t move toward the target area at all, you risk extinguishing the old behaviors and they will have to be learned all over again. Luckily, [Ben’s] cat was smart enough to figure it out.
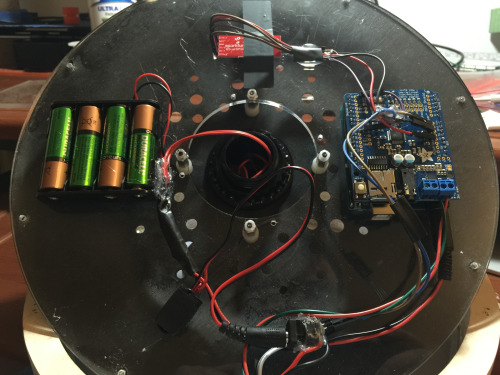
With the cat properly trained, it was time to build the cat feeder. [Ben] used an off-the-shelf electronic feeder called Super Feeder as the base for his project. The feeder is controlled by a relay that is hooked up to an Arduino. The Arduino is also connected to an RFID reader. Each plastic ball has an RFID tag inside it. When the cat places the ball into the target area, the reader detects the presence of the ball and triggers the relay for a few seconds. The system also includes a 315MHz wireless receiver and remote control. This allows [Ben] to manually dispense some cat food should the need arise.
Now whenever the cat is hungry, it can use those primal instincts to hunt for food instead of just having it freely handed over.
[Thanks Dan]
Filed under:
home hacks