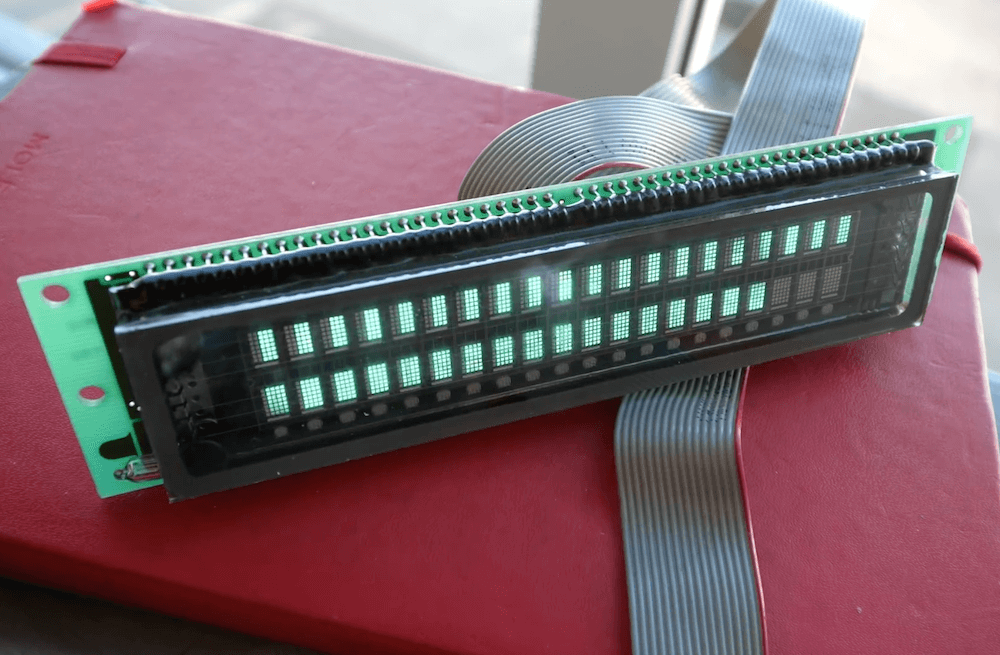
VFD Character Display Turned Into Audio VU Meter

Humans love visualising music, whether it’s in the form of an inscrutable equation drawing squiggles in Winamp, or a simple VU meter pulsing with the beat. This build from [mircemk] is of the latter variety, repurposing a VFD display to do the job.
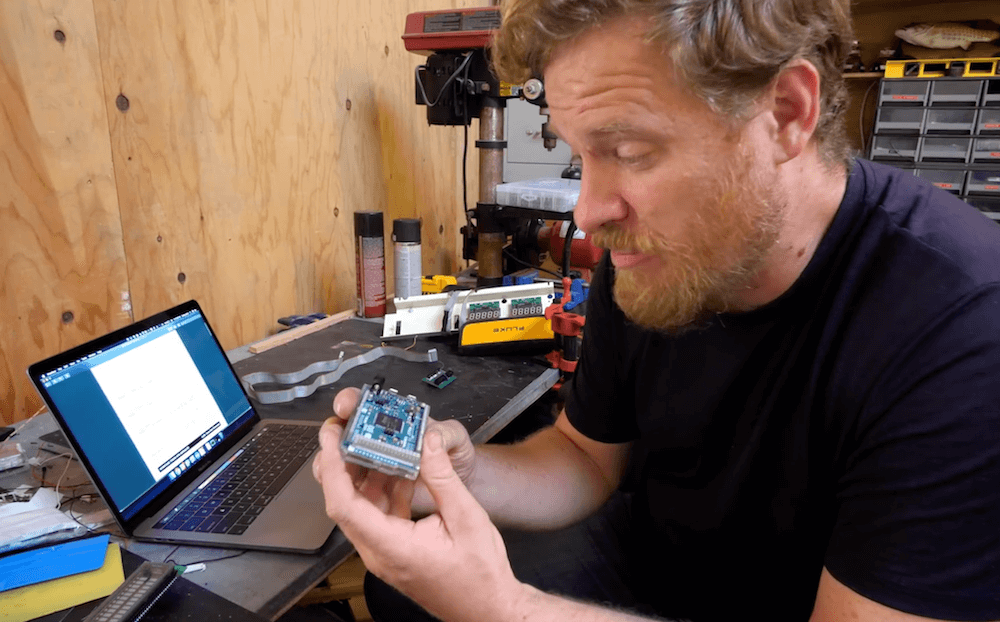
 The project is built around a VFM202MDA vacuum fluorescent display, which provides that lovely green-blue glow we all know and love, driven by a PT6314 driver chip. This has the benefit that it can be readily driven by a microcontroller in much the same way as the familiar HD44780 character LCD driver chip. With some minor tweaks, the character set can be modified to allow the display to become a surprisingly-responsive VU meter.
The project is built around a VFM202MDA vacuum fluorescent display, which provides that lovely green-blue glow we all know and love, driven by a PT6314 driver chip. This has the benefit that it can be readily driven by a microcontroller in much the same way as the familiar HD44780 character LCD driver chip. With some minor tweaks, the character set can be modified to allow the display to become a surprisingly-responsive VU meter.
An Arduino Nano runs the show, with an envelope follower circuit feeding a signal for the left and right channels into the analog inputs of the microcontroller. The Arduino then measures the voltage on those inputs and feeds the necessary commands to the PT6314 driver to update the display.
The resulting VU meter has 38 bars per channel, and is highly responsive. The fast flickering of the meter bars in response to the music make it compelling to watch, and the era-appropriate enclosure the project is built in adds plenty to the aesthetic.
We’ve seen other VU meter builds before too, like this one that uses a little physics knowledge to create a more realistic analog-like needle meter. Video after the break.