Glorious Body of Tracked ‘Mad Mech’ Started as Cardboard
[Dickel] always liked tracked vehicles. Taking inspiration from the ‘Peacemaker’ tracked vehicle in Mad Max: Fury Road, he replicated it as the Mad Mech. The vehicle is remote-controlled and the tank treads are partly from a VEX robotics tank tread kit. Control is via a DIY wireless controller using an Arduino and NRF24L01 modules. The vehicle itself uses an Arduino UNO with an L298N motor driver. Power is from three Li-Po cells.
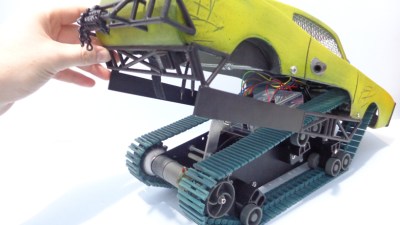 The real artistic work is in the body. [Dickel] used a papercraft tool called Pepakura (non-free software, but this Blender plugin is an alternative free approach) for the design to make the body out of thin cardboard. The cardboard design was then modified to make it match the body of the Peacemaker as much as possible. It was coated in fiberglass for strength, then the rest of the work was done with body filler and sanding for a smooth finish. After a few more details and a good paint job, it was ready to roll.
The real artistic work is in the body. [Dickel] used a papercraft tool called Pepakura (non-free software, but this Blender plugin is an alternative free approach) for the design to make the body out of thin cardboard. The cardboard design was then modified to make it match the body of the Peacemaker as much as possible. It was coated in fiberglass for strength, then the rest of the work was done with body filler and sanding for a smooth finish. After a few more details and a good paint job, it was ready to roll.
There’s a lot of great effort that went into this build, and [Dickel] shows his work and process on his project page and in the videos embedded below. The first video shows the finished Mad Mech being taken for some test drives. The second is a montage showing key parts of the build process.
Paper and cardboard are very versatile and accessible materials for making things. It’s what was used to do some target practice with this working paper and cardboard gun. With the right techniques foam core can be worked into an astonishing variety of shapes, and we also made a case for the value of a desktop vinyl cutter on any well-equipped hacker’s workbench.




