Little Lie Detector is Probably No Worse Than The Big Ones

Want to know if somebody is lying? It’s always so hard to tell. [dbmaking] has whipped up a fun little polygraph, otherwise known as a lie detector. It’s nowhere near as complex as the ones you’ve seen on TV, but it might be just as good when it comes to finding the truth.
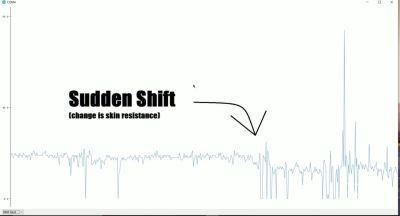
The project keeps things simple by focusing on two major biometric readouts — heart rate and skin conductivity. When it comes to the beating heart, [dbmaking] went hardcore and chose an AD8232 ECG device, rather than relying on the crutch that is pulse oximetry. It picks up heart signals via three leads that are just like those they stick on you in the emergency room. Skin conductivity is measured with a pair of electrodes that attach to the fingers with Velcro straps. The readings from these inputs are measured and then used to determine truth or a lie if their values cross a certain threshold. Presumably, if you’re sweating a lot and your heart is beating like crazy, you’re telling a lie. After all, we know Olympic sprinters never tell the truth immediately after a run.
Does this work as an actual, viable lie detector? No, not really. But that’s not just because this device isn’t sophisticated enough; commercial polygraph systems have been widely discredited anyway. There simply isn’t an easy way to correlate sweating to lying, as much as TV has told us the opposite. Consider it a fun toy or prop to play with, and a great way to learn about working with microcontrollers and biometric sensors.