Get Your Flex On With The FlowIO Platform

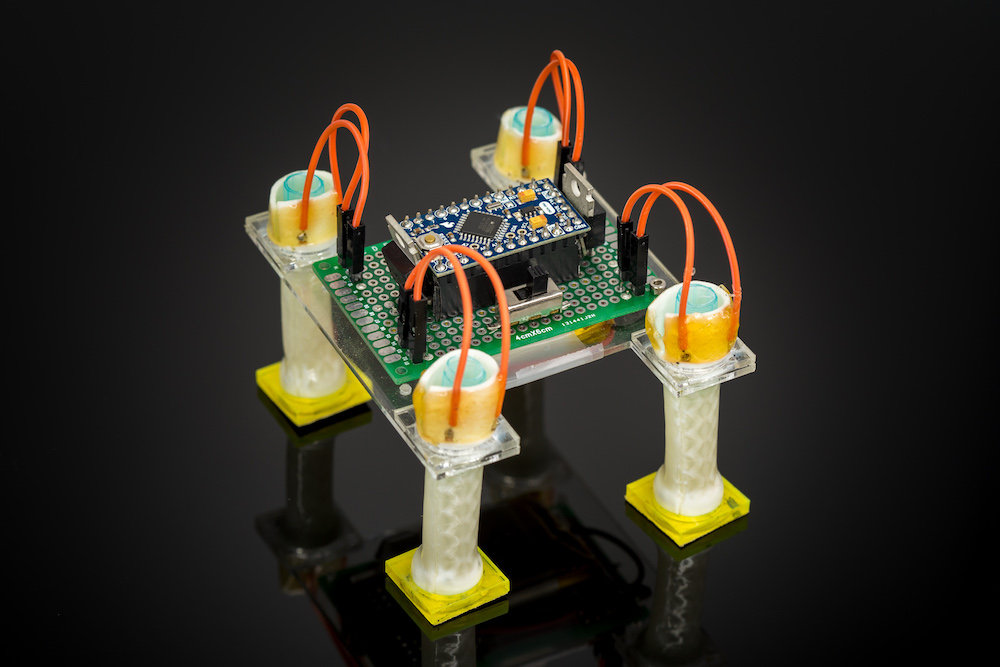
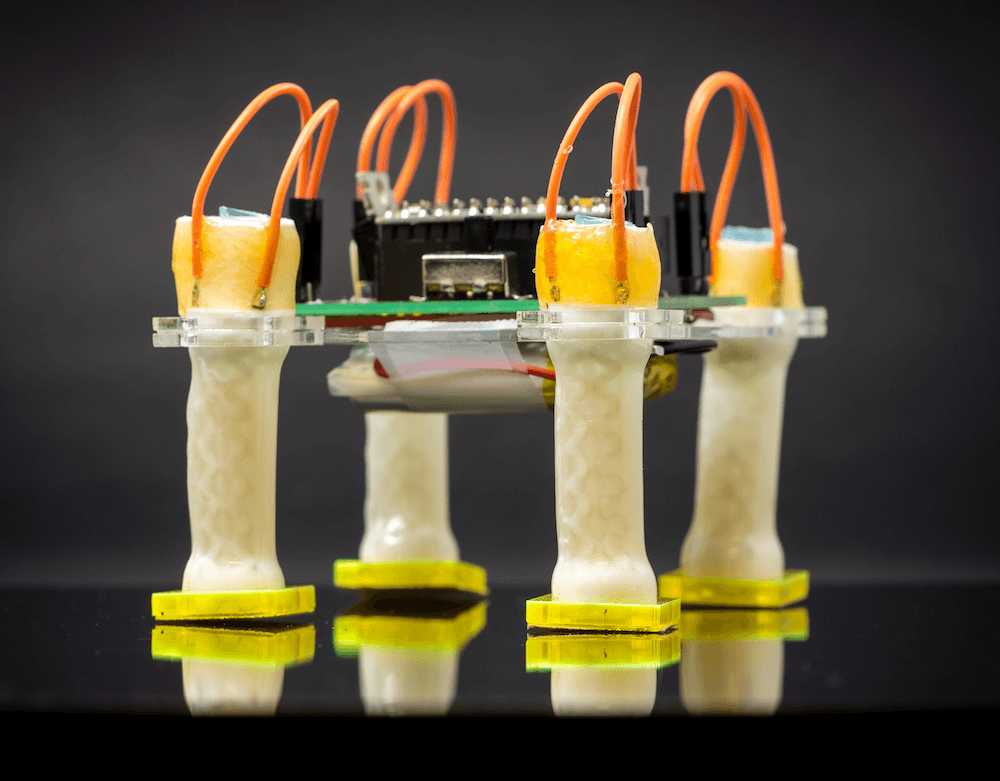
Hackaday Prize 2021 entry FlowIO Platform promises to be to pneumatics what Arduino is to Electronics. The modular platform comprises a common controller/valve block, a selection of differently sized pumps, and a few optional connectivity and sensing blocks. With Arduino software support as well as as Javascript and web-GUI, there’s a way to program this no matter what the level of experience the user has.

This last point is a critical one for the mission [Ali Shtarbanov] from the MIT Media Lab is setting out for this project. He reminds us that in decades gone by, there was a significant barrier to entry for anyone building electronics prototypes. Information about how to get started was also much harder to by before the internet really got into gear.
It’s a similar story for software, with tools like Scratch and Python lowering the barrier to entry and allowing more people to get their toes wet and build some confidence.
But despite some earlier work by projects like the Soft Robotics Toolkit and Programmable-Air, making a start on lowering the bar for pneumatics support for soft robotics, and related applications, the project author still finds areas for further improvement. FlowIO was designed from the ground-up to be wearable. It appears to be much smaller, more portable and supports more air ports and a greater array of sensing and connectivity than previous Open Source work to date.
Creative Commons Hardware
Whilst you can take all the plans (free account signup required) and build yourself a FlowIO rig of your very own, the project author offers another solution. Following on from the Wikipedia model of free sharing and distribution of information, FlowIO offers its hardware for free, for the common good. Supported by donations to the project, more hardware is produced and distributed to those who need it. The only ask is that redundant kits are passed on or returned to base for upgrade, rather than landfill.